Organisations
You can import and export an entire Flagsmith organisation. This lets you:
- Migrate from self-hosted Flagsmith to SaaS, or the other way around.
- Migrate from one self-hosted Flagsmith instance to another.
Merging data between existing Flagsmith organisations is not supported. A new Flagsmith organisation is created as part of the import process.
Prerequisites
Importing or exporting an organisation requires shell access to any machine or container where Flagsmith is installed and can connect to your Flagsmith database.
Organisations can be imported or exported using the local file system or S3-compatible storage.
Importing or exporting an organisation does not require downtime. However, it is a one-time operation that does not continuously migrate data. You should plan a convenient time to perform imports and exports.
If you need to copy an organisation from or to Flagsmith SaaS, please contact Flagsmith support.
What is exported?
We will export the following entities:
- Projects
- Flags
- Segments
- Identities
- Integrations
- Client-side and server-side SDK keys
We will not export the following entities:
- Flagsmith users
- Flag analytics
- Audit logs
- Change requests
- Scheduled flag changes
- Admin API keys
- Groups and custom roles
- SAML configurations and login method restrictions
Running shell commands
Importing or exporting is performed using shell commands on a Flagsmith container that has access to your Flagsmith database. You can also create a new container just for this operation.
Kubernetes
To run an interactive shell inside an existing API container, use kubectl exec replacing YOUR_API_SERVICE with the
name of your Flagsmith API Kubernetes service:
kubectl exec -it service/YOUR_API_SERVICE --container flagsmith-api -- sh
To find your Flagsmith API Kubernetes service, you can use kubectl get services:
kubectl get services --selector app.kubernetes.io/component=api
Putting these two commands together, this one-liner will give you an interactive API shell:
kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get service --selector app.kubernetes.io/component=api --output name) --container flagsmith-api -- sh
Docker Compose
Use docker compose exec to get an interactive shell inside your API container, replacing flagsmith with your
Flagsmith API service name from your Compose definition:
docker compose exec -it flagsmith sh
SSH and local environments
If you have a shell inside a Flagsmith environment, check that you can run python manage.py. In containers running
Flagsmith images, this file is located in the /app directory:
python /app/manage.py health_check
Exporting
To export your Flagsmith organisation, you need to know its ID. To find an organisation's ID, use one of the following methods:
- From the Flagsmith dashboard, click your organisation name in the top left. The organisation ID is displayed in
the URL bar:
https://flagsmith.example.com/organisation/YOUR_ORGANISATION_ID/.... - From Django Admin, browse to the Organisations section in the sidebar. Here you can see all of your organisations and their IDs.
- If you have an Admin API key, call the List Organisations API endpoint. This returns all the organisations that your API key is a member of.
Once you have shell access and you know the organisation's ID, you can export it to the container's file system or S3-compatible storage.
Exporting to the local file system
To export the organisation with ID 1234 to a JSON file in the local file system:
python manage.py dumporganisationtolocalfs 1234 /tmp/organisation-1234.json
Then, copy the exported JSON file to a secure location.
Kubernetes
From the same shell you exported the organisation from, run the hostname command to get the current pod name. For
example:
$ hostname
flagsmith-api-59d68fd74d-4kw2k
Then, from a different machine, use kubectl cp to copy the exported file for further processing:
kubectl cp --container flagsmith-api YOUR_API_POD_NAME:/tmp/organisation-1234.json ~/organisation-1234.json
Read-only file systems
In some situations, you may not be able to write to /tmp or any directory in the container's root file system. If
this is the case, attach a writable volume to your API pods. For example, if you are using the Flagsmith Helm chart:
api:
extraVolumes:
- name: exports
emptyDir: {}
volumeMounts:
- name: exports
mountPath: /exports
Then, export your organisation to this directory and copy it following the previous steps.
Docker
From the same shell you exported the organisation from, run the hostname command to get the container ID. For example:
$ hostname
6893461b8a7e
Then, from the host machine, copy the exported file from the container using docker cp. For example:
docker cp 6893461b8a7e:/tmp/organisation-1234.json .
Exporting to S3-compatible storage
To export the organisation with ID 1234 to a key named 1234.json in the S3 bucket named my-bucket:
python manage.py dumporganisationtos3 1234 my-bucket 1234.json
You can provide additional S3 configuration for authentication or to use services other than AWS S3.
Importing
You can import an organisation from the local file system or S3-compatible storage.
Importing from the local file system
To import the organisation exported in the file /tmp/org-1234.json, run this command from a Flagsmith container:
python manage.py loaddata /tmp/org-1234.json
Importing from S3-compatible storage
To import the organisation exported in the key org-1234.json of the AWS S3 bucket named my-bucket, run this command
from a Flagsmith container:
python manage.py importorganisationfroms3 my-bucket org-1234.json
You can provide additional S3 configuration for authentication or to use services other than AWS S3.
Accessing an imported organisation
After you import an organisation, you will need to add your Flagsmith user to it. To do this, edit the imported organisation from Django Admin and add your user to it with Admin permissions:
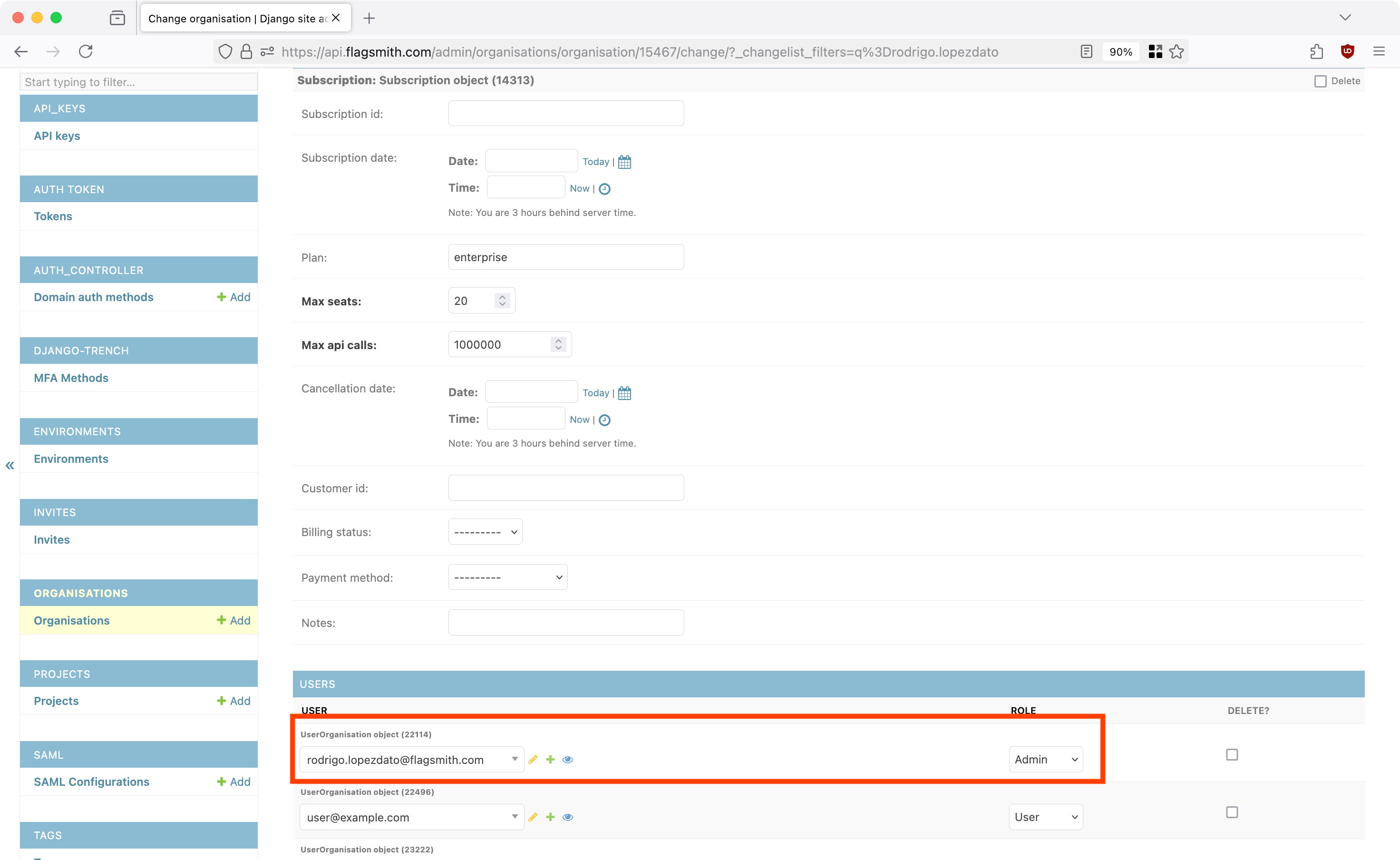
Additional S3 configuration
To provide credentials, set the AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY environment variables before running
any commands. For example:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='abc123'
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY='xyz456'
By default, all commands will interact with buckets hosted on AWS S3. To use other S3-compatible services such as Google
Cloud Storage, set the AWS_ENDPOINT_URL_S3 environment variable:
export AWS_ENDPOINT_URL_S3='https://storage.googleapis.com'